
In Teton County, Idaho, a region rich in natural beauty and diverse ecosystems, it is important to understand the distinctions between wetlands and floodplains. These unique environments play significant roles in the local ecology and provide valuable benefits. To shed light on these differences, we turn to the Land Development Code of Teton County, Idaho, which outlines specific definitions, regulations, and guidelines for managing these essential habitats.
Definitions and Identification:
Wetlands: According to the Teton County Land Development Code, wetlands are defined as areas that are inundated or saturated by surface water or groundwater, supporting vegetation adapted to saturated soil conditions. Wetlands in Teton County are classified into four categories: riparian wetlands, seep wetlands, groundwater discharge wetlands, and marsh wetlands. These classifications help identify and differentiate various wetland types based on their hydrology, vegetation, and ecological characteristics. Wetlands in Teton County exhibit unique hydrological characteristics. They are typically associated with a high water table, resulting in saturated or waterlogged soils. Wetlands receive water from various sources, including precipitation, surface water, and groundwater. They may have standing water throughout the year or experience seasonal fluctuations. Wetlands play a vital role in water storage and filtration, promoting groundwater recharge and improving water quality.
Floodplains: Floodplains in Teton County refer to the land area adjacent to rivers, streams, or other water bodies that are subject to inundation during flooding events. The Land Development Code recognizes the importance of floodplains in regulating floodwaters, reducing flood hazards, and protecting water quality. The code defines a Flood Hazard Overlay District, which outlines regulations for development within flood-prone areas to minimize the potential risks associated with flooding. Floodplains, as defined by the Land Development Code, primarily pertain to the risk of flooding. These areas are subject to periodic inundation during high water flow events, such as heavy rainfall or snowmelt. Floodplains act as natural flood buffers, absorbing and temporarily storing excess water. They facilitate the gradual release of floodwaters, reducing the impact on downstream areas. The dynamic water flow in floodplains helps deposit sediments and nutrients, enhancing soil fertility.
Ecological Significance and Conservation:
Teton County recognizes the ecological importance of wetlands and floodplains, and their role in maintaining biodiversity. They provide critical habitats for a variety of plant and animal species, including migratory birds, amphibians, and rare vegetation. Wetlands also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change impacts, while floodplains promote natural processes, such as nutrient cycling and sediment deposition, which contribute to ecosystem health. The Land Development Code emphasizes the protection and conservation of these by encouraging responsible land management practices to minimize the impact of development on these areas.
Regulatory Measures and Human Interaction:
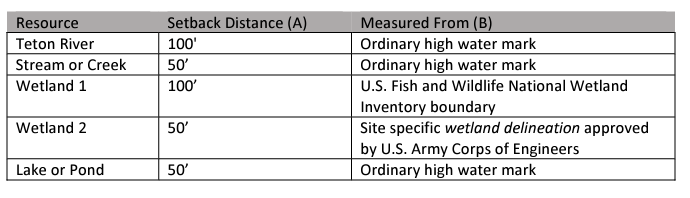
Wetlands: Teton County has established regulations to protect wetlands from adverse impacts. The Land Development Code outlines provisions for wetland setbacks, which require maintaining a certain distance between development activities and wetland boundaries. It also promotes wetland restoration and enhancement efforts to preserve and restore the functions and values of these valuable ecosystems. Chapter 5 of the Land Development Code defines the setbacks for development from various waterways, and what type of development are permitted and prohibited within these Riparian Buffers.
Definitions and Identification:
Wetlands: According to the Teton County Land Development Code, wetlands are defined as areas that are inundated or saturated by surface water or groundwater, supporting vegetation adapted to saturated soil conditions. Wetlands in Teton County are classified into four categories: riparian wetlands, seep wetlands, groundwater discharge wetlands, and marsh wetlands. These classifications help identify and differentiate various wetland types based on their hydrology, vegetation, and ecological characteristics. Wetlands in Teton County exhibit unique hydrological characteristics. They are typically associated with a high water table, resulting in saturated or waterlogged soils. Wetlands receive water from various sources, including precipitation, surface water, and groundwater. They may have standing water throughout the year or experience seasonal fluctuations. Wetlands play a vital role in water storage and filtration, promoting groundwater recharge and improving water quality.
Floodplains: Floodplains in Teton County refer to the land area adjacent to rivers, streams, or other water bodies that are subject to inundation during flooding events. The Land Development Code recognizes the importance of floodplains in regulating floodwaters, reducing flood hazards, and protecting water quality. The code defines a Flood Hazard Overlay District, which outlines regulations for development within flood-prone areas to minimize the potential risks associated with flooding. Floodplains, as defined by the Land Development Code, primarily pertain to the risk of flooding. These areas are subject to periodic inundation during high water flow events, such as heavy rainfall or snowmelt. Floodplains act as natural flood buffers, absorbing and temporarily storing excess water. They facilitate the gradual release of floodwaters, reducing the impact on downstream areas. The dynamic water flow in floodplains helps deposit sediments and nutrients, enhancing soil fertility.
Ecological Significance and Conservation:
Teton County recognizes the ecological importance of wetlands and floodplains, and their role in maintaining biodiversity. They provide critical habitats for a variety of plant and animal species, including migratory birds, amphibians, and rare vegetation. Wetlands also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change impacts, while floodplains promote natural processes, such as nutrient cycling and sediment deposition, which contribute to ecosystem health. The Land Development Code emphasizes the protection and conservation of these by encouraging responsible land management practices to minimize the impact of development on these areas.
Regulatory Measures and Human Interaction:
Wetlands: Teton County has established regulations to protect wetlands from adverse impacts. The Land Development Code outlines provisions for wetland setbacks, which require maintaining a certain distance between development activities and wetland boundaries. It also promotes wetland restoration and enhancement efforts to preserve and restore the functions and values of these valuable ecosystems. Chapter 5 of the Land Development Code defines the setbacks for development from various waterways, and what type of development are permitted and prohibited within these Riparian Buffers.
Floodplains: Teton County's Flood Hazard Overlay District provides regulations for development within floodplain areas to ensure public safety and minimize flood risks. These regulations include requirements for floodplain analysis, building elevation standards, and flood-resistant design. The code aims to balance development needs with floodplain conservation, encouraging responsible land use practices while preserving the natural functions of floodplains.
Understanding the distinctions between wetlands and floodplains is crucial for effective land management and environmental conservation in Teton County, Idaho. The Land Development Code provides valuable insights into the definitions, characteristics, and regulations governing these unique ecosystems. By recognizing the ecological significance of wetlands and floodplains and implementing appropriate measures, Teton County aims to maintain the delicate balance between human development and the preservation of these vital habitats for current and future generations.
Understanding the distinctions between wetlands and floodplains is crucial for effective land management and environmental conservation in Teton County, Idaho. The Land Development Code provides valuable insights into the definitions, characteristics, and regulations governing these unique ecosystems. By recognizing the ecological significance of wetlands and floodplains and implementing appropriate measures, Teton County aims to maintain the delicate balance between human development and the preservation of these vital habitats for current and future generations.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
